Tumors – formations on the body, resulting from the violation of the mechanisms of control of division, growth of body cells.
Generally all tumors can be divided into two large groups: Benign and malignant.
Benign tumors.
- Adenoma,
- Fibroma,
- Lipoma,
- Leiomyoma,
- Osteoma,
- Neuroma,
- Rhabdomyoma
Benign tumors grow slowly, gradually squeezing the surrounding structures and tissues, but never penetrate them. They tend to respond well to surgery and rarely recur.
Malignant tumors are characterized by rapid and aggressive growth and the ability to germinate in the surrounding organs and tissues, blood and lymphatic vessels with the formation of metastases. Malignant tumors are usually difficult to treat and often recur. The prognosis of the disease in the presence of metastases in distant organs is unfavorable. (Oncology section)
The type of treatment depends on the type of tumor, its localization and the general condition of the patient. Surgical removal is the most effective method of tumor treatment. In the case of benign tumors, the recurrence rate of the tumor after surgical treatment is small.
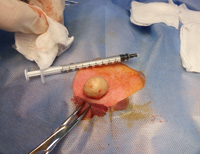
Surgery
Surgical removal of benign soft tissue formations (lipomas, atheromas, fibromas) is performed under local anesthesia with the imposition of a cosmetic suture. The procedure takes 15-20 minutes, hospitalization is not required.
Radio wave removal of benign soft tissue formations (papillomas, warts, dry callus) is performed under local anesthesia using “Surgitron” apparatus. The procedure takes 15-20 minutes, hospitalization is not required.












